In the urinary system, the bladder plays the role of a collector storage collector: exhausted blood filter products come from the kidneys through the ureters.It is thanks to the bladder and two muscle rings, one of which obeys the conscious commands of the central nervous system, a healthy person can carry out urination as necessary, necessity and opportunity.The "possibility" in the early stages of evolution was destined, in the first place, a safe atmosphere;With the advent and development of human civilization, urine began to demand special conditions, that is, a break in social activity, a specially designed and/or loneliness of representatives of the opposite sex.
Cystitis is an inflammatory process on the internal walls of the bladder;A disease that causes pronounced physiological and psychological discomfort, as well as a certain social maladjustment.A person of any age and gender can face this misfortune, but it is no coincidence that cystitis is sometimes called a curse of a modern woman (it would be more correct to say "one of the curses", since this is not the only disease of this type).The main reason lies in anatomy: compared to the male female urethra (urethra) is much shorter, more elastic, wider and more straight.This creates extremely convenient "doors" for the penetration of ascending urogenital infections, whose prevalence and variety in the modern world is really very large.And although not all cystitis have an infectious nature, it is the described mechanism of their development that is a key factor in epidemiological differences between singles: according to different sources, in women of active age, cystitis occurs 6-8 times more often than in men.
In general, statistical analysis allows you to evaluate the problem in a variety of angles.Then, many sources indicate that at least a single cystitis attack during life is experiencing at least half of all women;At least, each room is periodic or chronic (some authors even consider these very low data, since not all sick people look for a doctor).According to medical documentation, in clinics, among all urological patients, the proportion of patients with cystitis reaches 67%;In urological hospitals, this indicator is 5-12% (in other words, the percentage of hospitalization in cystitis is also very high, which once again confirms the social importance of this disease).The frequencies of acute and chronic forms are approximately 2: 1.
The difference in the incidence between the floors is leveled to the age of elders and seniles: in the elderly categories, the proportion of primarily sick men with cystitis is comparable to a similar percentage of women.But in a mature, young, young age (and, sometimes, in adolescence or even in a child), when to live, it seems to rejoice!- Cystitis is waiting and chooses mainly women.
Reasons
Of the infections, the bladder wall is protected by nature, in principle, well enough;The predominance of the infectious etiology of cystitis is not due to vulnerability as such, but through a combination of a high probability of infection with external and internal adverse conditions, most of which are somehow connected with the way of life.The Main Risk Factors Include Any Acute and Chronic Infections in Other Body Systems (From Caries and Colitis To Acute Respiratory Viral Infections - Sexually Transmitted Diseases), Hypothermia, Hypovitaminosis, After Surgical Depletion, Unahealthy Diet, OverworDeficiety, psycho -Emotional stresses, Random sex (specially "non -traditional" "and extreme practices), preference for synthetic linen, insufficient hygiene (it is difficult to imagine how hygienic skills and needs can be insufficient in the 21st century, and yet this factor remains significant).Sexes, we mention another, in addition to the anatomical, the cause of endocrine fluctuations, namely, the fluctuations of the hormonal background (in particular, the exacerbations of the cystitis associated with the phase of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy or menopause are considered separate in literature).
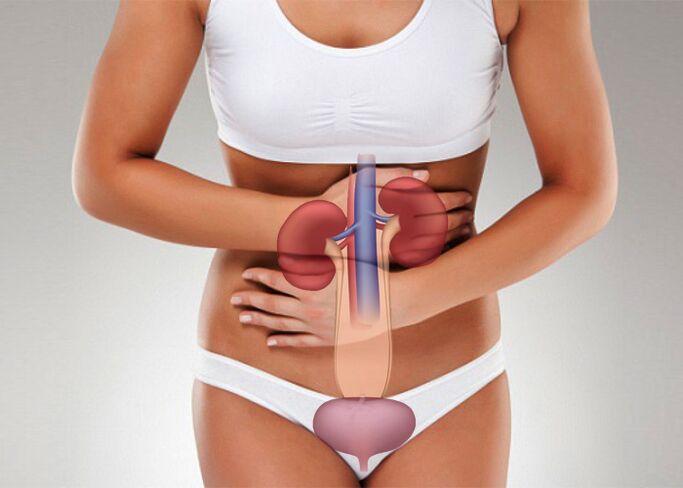
We also observe that the infection can penetrate the bladder not only ascending, but also by descending paths, from the kidney affected by nephritis.
Non -infectious forms include chemical toxic (including medications), allergic, radiation, traumatic, parasite.
Symptoms
The classic symptoms of cystitis include, in the first place, intensive discomfort during urination: rubbing, pain, ardor, etc.Often, urine leaves the feeling that the bladder is not completely empty;Many patients complain of a repeated or false impulse, observe the "escape" of linen or the imperative nature of the impulse (because, again, the anatomical reasons are more inherent to women who often "do not have time to run" and, therefore, are forced to stay constantly closer to the toilet).In some cases, the cloud or a mixture of blood is revealed in the urine;It should be said that hematuria is the most dangerous urological symptom and requires an immediate differential diagnosis, since the presence of blood in the urine can be caused not only by cystitis, but also by the causes of life.
It is typical and, as a rule, is severely expressed with cystitis of pain syndrome: throw or spicy, explode or pain in the lower part of the abdomen, often with irradiation in the crotch or back.Without such similar or similar pain, no more than 10% of all cystitis procedures.With a sufficient immune response, general discomfort, fever, weakness, headache are often intense.
The most likely and serious complications of cystitis include the SO, called its interstitial shape, when not only the mucosa, but also a deeper muscular layer of the bubble walls is involved in the inflammatory process (ultimately, this can lead to the withdrawal of the bubble and its indicated failure), as well as the propagation of infection by adjacent organes, where it can cause very much, where it can cause very much, where it can cause very much, where it can cause very much, where it can be very veryGraves to the bubble (pyelelenemhitis), such as the spread of infection by the adjacent organs, where it can cause very serious to the bubble (pyelelenemhitis), as well as the propagation of infection by adjacent organs, where it can cause very serious, very serious to the bubble (pyellelenemhitis), as well as the propagationof infection by adjacent organs.infertility, etc.).
Diagnosis

In addition to a clinical survey and a standard urological inspection (however, many women prefer to treat cystitis not a urologist, but to "their" gynecologist), laboratory tests are mainly prescribed.To date, much of all kinds of methods to detect the pathogen are used successfully;As previously shown, the most likely cause should always be considered a bacterial, viral or fungal infection.As a need for diagnosis, ultrasound is also prescribed, less than cystoscopy, less than cystography, biopsy and other studies.
Diagnosis
In addition to a clinical survey and a standard urological inspection (however, many women prefer to treat cystitis not a urologist, but to "their" gynecologist), laboratory tests are mainly prescribed.To date, much of all kinds of methods to detect the pathogen are used successfully;As previously shown, the most likely cause should always be considered a bacterial, viral or fungal infection.As a need for diagnosis, an ultrasound, an internal study of the bladder, an X -ray study of the bladder, biopsy and other studies is also prescribed.
Treatment
Acute cystitis in chronic turns often, easily and insidious: the gradual reduction of symptoms, even its complete disappearance, does not mean recovery at all.Therefore, the signs of cystitis described above in any of their combinations (especially because these symptoms are inherent to many other urological diseases) require an immediate visit to the doctor, and not to the patient's expectations, while "happens."Along the way, we observe that a large amount of good, intelligent, friendly, tested for centuries and other similar tips on the Internet (where you can find recommendations in the range of quite reasonable to schizophrenic or fraudulent) is one of the factors of the frequent chronicle and the complications of the cystitis.
Based on the results of the diagnostic exam, a particular treatment regime and always strictly individual is always prescribed, directly directs to eliminate the cause of inflammation.In different cases, antibiotics, antivirals, antimicotic drugs, immunomodulators and immunostimulants, antihistamines and anti -inflammatory drugs, and antispasmodic drugs can be used.The sanitation of chronic infection foci in other areas is required, as well as the treatment of background diseases (nephrolithiasis, prostate adenoma, etc.).In addition, a diet is required, greater fluid intake and savings regime to avoid hypothermia and other risk factors.Phytotherapeutic agents are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, and he also controls the effectiveness of his administration.
Subject to these conditions, cystitis is cured.






























